What is the Difference Between a Vial and a Tube for Laboratory Use?
2026 Feb 9th
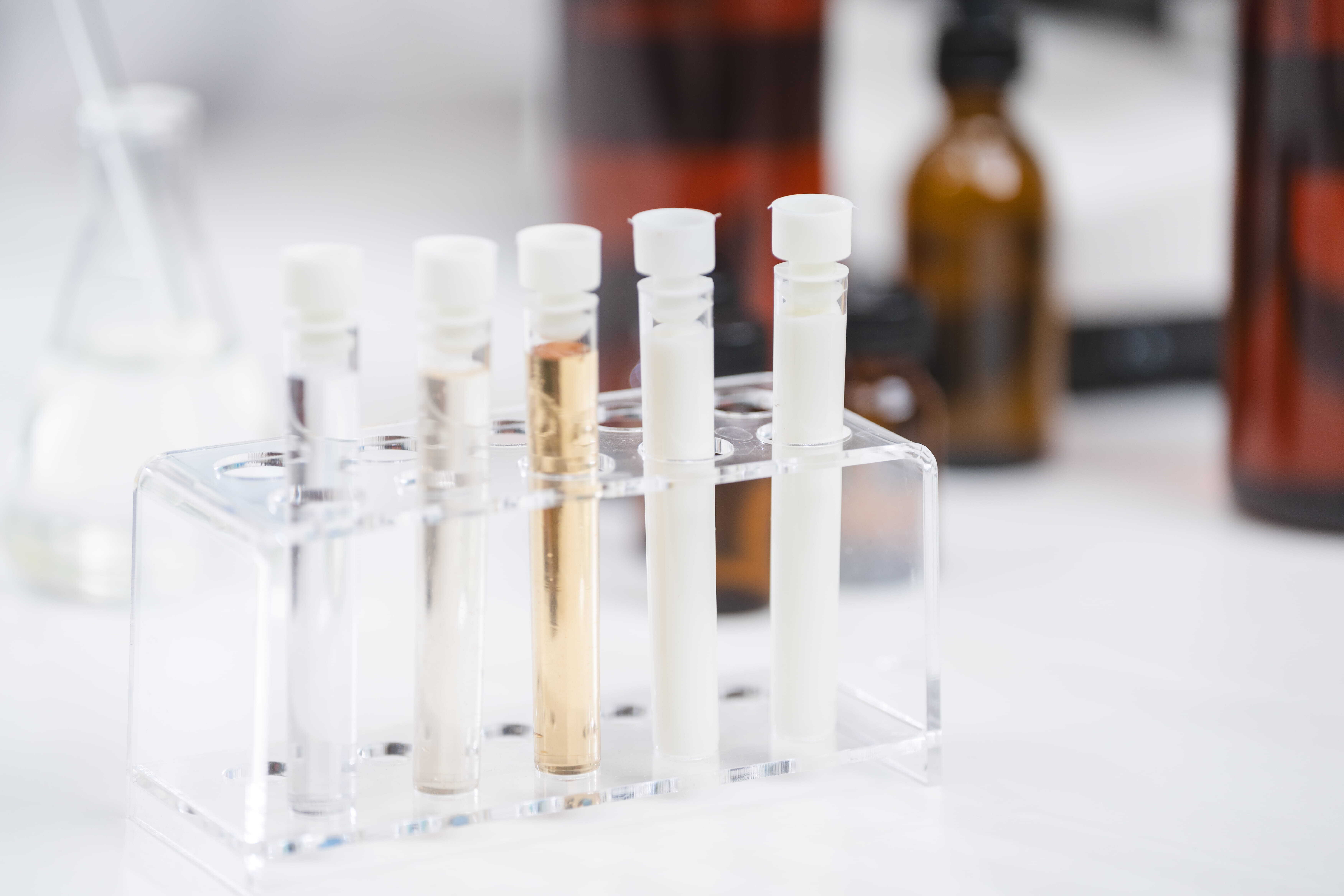

Understanding the difference between vials and tubes in the laboratory environment is vital. The wrong choice of laboratory tools can impact reliable results, samples, workflow efficiency, and most importantly, put workers in danger.
Vials and tubes are considered the most important lab consumables in a laboratory. According to this market analysis report referencing the global laboratory consumables market size, “the vials & containers segment held the largest share of 15.06% in 2024, driven by increasing demand for sustainable and functional packaging solutions.”
This article explains the difference between vials and tubes in laboratory environments. The aim is to support you in your choice to enhance reliable laboratory results, sampling, and protect workers.
Key Differences
Known as a valuable lab consumable, vials and tubes differ in multiple ways, from function, design, volume range, to typical applications in the laboratory.
Design & Closure Types
Due to their use in the medical, pharmaceutical, and scientific sectors, vials and tube designs differ in shape and closures. Although vials and tubes differ, both can be made from glass or plastic. The key differences between the two lab consumables in design and closure types are as follows:
- Vials: Small, often flat-bottomed containers made from high-quality, chemical-resistant glass such as borosilicate have been designed for secure, long-term storage in the medical sector, from reagents, medications, to samples.
Typically, vials feature screw caps to prevent contamination or evaporation.
- Tubes: Often, test tubes are larger, cylindrical, and round-bottomed. Conical containers have been designed for holding, mixing, or heating substances during laboratory experiments.
Tubes usually have open tops or use snap-caps or plugs.
Volume Range & Materials
Volume range and materials are used differently across tubes and vials, as each lab consumable is used for alternative methods and sectors.
- Vials: For small-volume storage (<1 mL to 40 mL), the smaller volume supports laboratories to measure precise, high-value samples. Alternative vials used in laboratory environments include microvials used in molecular biology that can hold between 0.5 mL and 2 mL.
- Tubes: For larger-volume storage (5 mL to 50 mL or more), this supports mixing, vortexing, and use in water baths. Alternative tubes used in laboratory environments include culture and centrifuge tubes that can hold 15 mL or more.
Typical Applications
From day-to-day tasks, storing samples, to conducting chemical reactions, vials and tubes vary in their typical applications.
- Vials: Used for storing, preserving, and protecting samples from cross-contamination and environmental exposure. Vials are typically used for high-precision tasks such as chromatography or storing powder and tissue samples, due to their secure closures, which reduce sample loss and variability
- Tubes: Used regularly for everyday tasks. Ideal for mixing reagents, conducting reactions, and growing microbial cultures due to their larger volume.

When to Use Each
Tubes and vials remain the backbone of lab consumables; each piece of equipment is used differently across each sector, from the pharmaceutical and medical field to daily scientific research.
According to research from this market analysis report, “the clinical diagnostics segment held the largest share of [global laboratory consumables at] 27.22% in 2024.” This growth reflects increased demand for standardized, automation-compatible consumables in clinical and research labs.
Common Uses for Vials
- Pharmaceutical & medical: Vials are used for injectable medication storage, multi-dose and single-dose containers, diagnostic samples, and eye drops.
- Scientific research: Vials are the best choice for chemical, reagent, and cryogenic storage, DNA/RNA samples, and autosampling.
Common Uses for Tubes
- Pharmaceutical & medical: Choose tubes for accuracy and safe blood, urine, saliva, and reagent storage.
- Microbiology & cell culture: Tubes are the best choice for microorganisms, bacteria, and cell growth.
- Scientific research: Tubes are used for mixing, heating, and observing chemical reactions.

Practical Considerations
Essential in the management and choice of lab consumables, practical considerations across tubes and vials ultimately impact the accuracy of scientific research, safety, cost-effectiveness, and operational workflow. We’ve compiled our top tips across compatibility, handling, and labelling:
Compatibility with Instruments & Storage
- For both tubes and vials, use screw-cap closures with secure seals rather than snap caps, as they are better suited for long-term storage.
- When handling cell cultures and microbiological samples, select pre-sterilized (gamma-irradiated) tubes to minimize the risk of contamination.
- Prior to use, confirm that the vial and tube dimensions are compatible with robotic and automated handling systems to help prevent workplace accidents and cross-contamination.
- Avoid using non-vented vials in the liquid phase of nitrogen, as rapid pressure buildup during thawing can cause them to rupture.
- Maintain 10–15% headspace in each container to allow for sample expansion during freezing.
Handling & Labeling
- For both vials and tubes, use labels that are resistant to extreme temperatures and chemical solvents.
- Barcoding tubes is recommended for efficient, high-throughput, and automated sample tracking.
- Always label both the side of the tube and the top of the cap, as caps may become separated from their containers.
- Inspect all tubes for cracks or defects before use, especially when they will be subjected to high-speed centrifugation.
- Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves and face shields, should always be worn when handling frozen or hazardous chemicals in tubes and vials.
Now that you have all the practical considerations and understand the main differences to consider for the laboratory, you are ready to make your choice between tubes and vials.
Quick Guidance on Choosing Between Vials & Tubes
Choosing the correct lab consumables, from tubes to vials, can support your laboratory research with reliable results and enhance your workflow efficiency with better worker safety.
You can explore our entire collection of tubes and vials once you are ready. If you are unsure which lab product best suits your laboratory, you can speak to our expert team.