Understanding Laboratory Safety Equipment: A Guide for Labs
2025 Apr 4th
Laboratory safety is a cornerstone of effective scientific research and operations, ensuring that personnel can perform their work in a controlled, hazard-free environment. The risks inherent to laboratory work—ranging from exposure to hazardous chemicals and pathogens to risks of fire and mechanical injury—necessitate the use of robust safety protocols and high-quality personal protective equipment (PPE). For experienced scientists and lab managers, understanding the nuances of lab safety equipment is not just a regulatory requirement but an operational imperative. This guide delves into the critical components of lab safety equipment and explores recent legislative updates in Canada to help labs maintain the highest standards of safety and compliance.
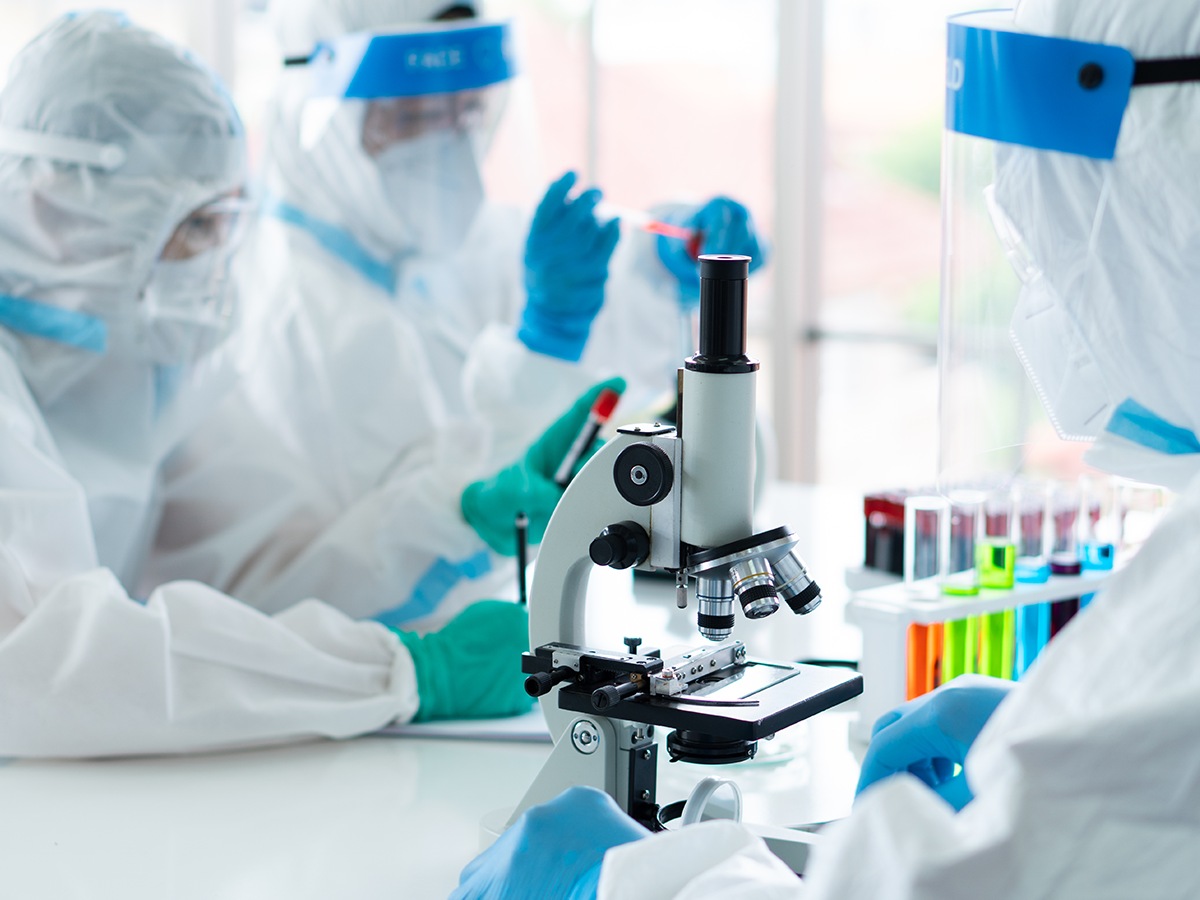

The Role of Lab Safety Equipment in Risk Mitigation
In the context of high-stakes research, lab safety equipment acts as a multifaceted barrier against a variety of threats. The effectiveness of safety measures depends on proper hazard assessments, selection of appropriate PPE, and adherence to operational protocols. For experienced professionals, the challenge often lies in integrating advanced safety measures into workflows without disrupting productivity.
Key Lab Safety Equipment: Technical Specifications and Applications
1. Protective Eyewear: Goggles and Face Shields
First and foremost, and perhaps obvious: Protective eyewear. It is indispensable in safeguarding against chemical splashes, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, and mechanical debris. Advanced safety goggles should feature anti-fog coatings, impact-resistant polycarbonate lenses, and compliance with ANSI Z87.1 or CSA Z94.3 standards. Face shields, often used in tandem with goggles, provide an extended barrier for high-risk procedures involving volatile reactions or the use of cryogenic liquids.
Application Example: During high-energy reactions such as exothermic chemical synthesis, face shields with anti-static and anti-scratch coatings are recommended to enhance visibility and durability.
2. Lab Coats and Protective Garments
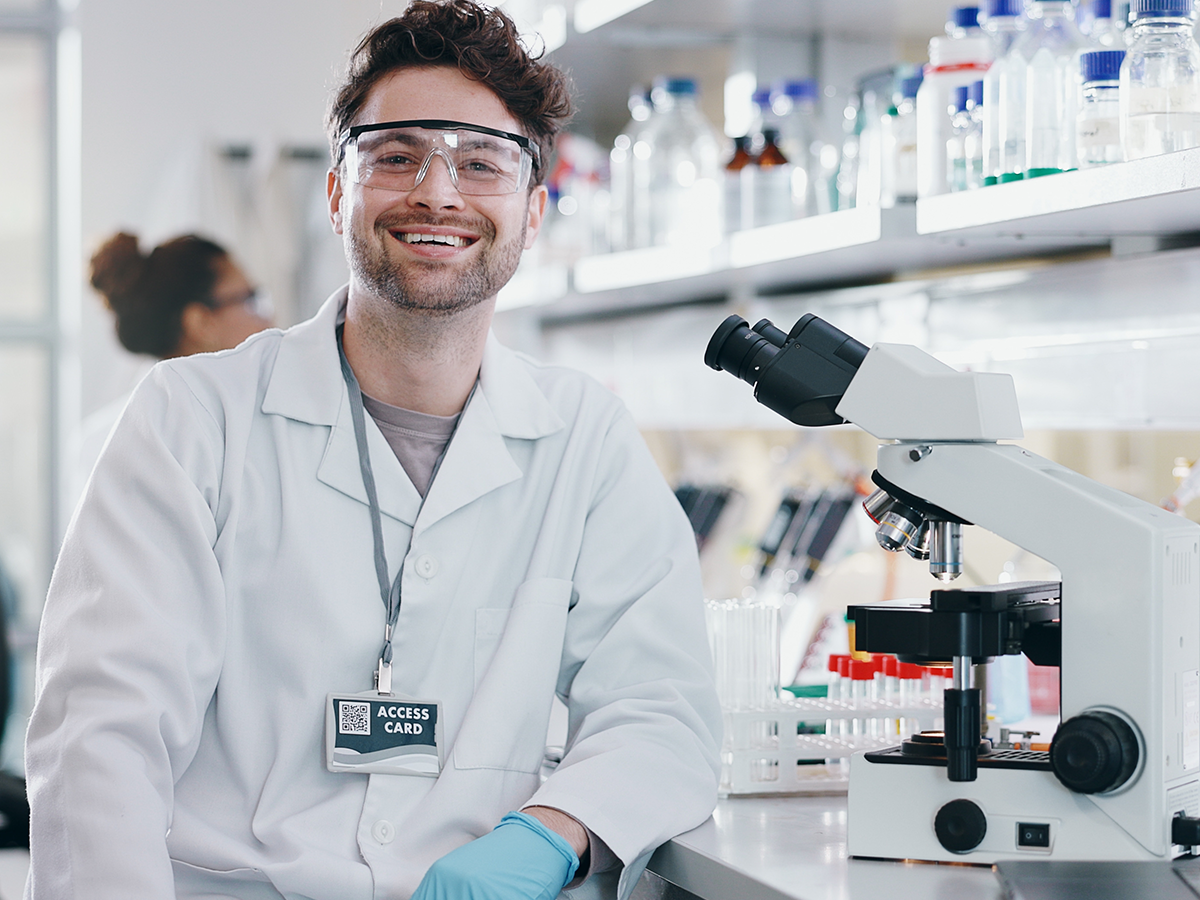 Modern lab coats have come a long way since the basic white tunic-like coat. Now they are engineered with advanced textiles, offering resistance to chemical permeation and fire retardation. The future of lab coats looks promising, and development from the soft antibacterial fabric with additional pockets for instruments.
Modern lab coats have come a long way since the basic white tunic-like coat. Now they are engineered with advanced textiles, offering resistance to chemical permeation and fire retardation. The future of lab coats looks promising, and development from the soft antibacterial fabric with additional pockets for instruments.
A textile researcher named Gerhard Mohr, along with a team at Joanneum Research Institute in Austria, is developing textiles that change colour when exposed to toxic or dangerous substances. This could be transformative for the field, especially when the lab coat responds to substances that could burn the skin or react to scentless poisonous gases such as carbon monoxide.
For labs handling corrosive substances, aprons made of neoprene or butyl rubber provide additional protection. Specialized garments, such as disposable Tyvek suits, are crucial in environments with biohazard risks.
Technical Note: Lab coats should conform to ISO 6530 standards for resistance to liquid chemicals. Multi-layer construction with reinforced seams offers extended durability under rigorous conditions.
3. Hand Protection: Specialized Gloves
Choosing the correct gloves is critical for precise hazard mitigation. Advanced materials and manufacturing techniques have yielded gloves with enhanced barrier properties, dexterity, and durability.
Nitrile Gloves: Engineered to resist punctures and a wide spectrum of chemicals, these gloves are preferred for organic solvent handling.
Latex Gloves: While offering superior elasticity and tactile sensitivity, their use is restricted in facilities due to latex allergy concerns. Non-latex alternatives such as chloroprene are increasingly utilized.
Cryogenic Gloves: Designed for handling ultra-cold materials, these gloves must meet ASTM F903 standards for permeation resistance.
Application Example: Handling concentrated hydrofluoric acid requires nitrile gloves with extended cuffs, certified under EN ISO 374-1 for chemical risks.ootwear should meet CSA Z195 standards for protective shoes, ensuring adequate impact and chemical resistance.
4. Respiratory Protection
Respiratory equipment serves as a barrier against inhalation hazards such as aerosols, particulates, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Laboratories must implement respiratory protection programs in accordance with CSA Z94.4 standards.
Types:
Powered Air-Purifying Respirators (PAPRs): Suitable for environments with sustained airborne contamination.
Chemical Cartridge Respirators: Designed for specific organic vapour and acid gas filtering.
Advanced Features: Devices equipped with end-of-service-life indicators (ESLI) and multi-stage filtration provide enhanced safety and operational efficiency.
5. Protective Footwear
Footwear designed for laboratory use must combine ergonomic comfort with resistance to chemical spills and mechanical hazards. Steel-toe or composite-toe boots with slip-resistant outsoles are ideal for facilities with heavy equipment or frequent handling of corrosive agents. Footwear should meet CSA Z195 standards for protective shoes, ensuring adequate impact and chemical resistance.
6. Emergency Decontamination Equipment
Emergency showers and eyewash stations are crucial for mitigating exposure to hazardous substances. These systems must adhere to ANSI Z358.1 standards, ensuring a minimum flow rate of 20 litres per minute for showers and 1.5 litres per minute for eyewash stations.
Periodic Testing: Canadian regulations mandate weekly functional testing of these units to ensure operational readiness. Advanced systems with self-cleaning nozzles and temperature control reduce maintenance overhead.
Legislative Framework and Updates
Canada’s regulatory landscape for laboratory safety is defined by both federal and provincial statutes, including the Canada Labour Code and the Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Regulations. Recent amendments have placed a greater emphasis on PPE customization, training documentation, and hazard-specific risk assessments.
Key Regulatory Updates:
Hazard Communication: The adoption of the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) for chemical labelling and safety data sheets (SDS) requires updated training for all lab personnel.
Fit Testing for Respirators: Provinces such as Ontario now mandate quantitative fit testing for all tight-fitting respirators.
Maintenance Protocols: Enhanced guidelines require detailed records of PPE inspections and routine equipment servicing.
Risk Assessments
To align with regulatory expectations, labs must conduct thorough risk assessments that evaluate potential hazards for each experimental protocol. This includes:
Identifying chemical incompatibilities.
Assessing the efficacy of PPE under simulated exposure conditions.
Documenting mitigation strategies for high-risk procedures.
Advanced Safety Solutions from Delta
For seasoned professionals, maintaining laboratory safety is a dynamic challenge requiring both technical expertise and access to high-quality safety equipment. By leveraging advanced PPE and staying informed about evolving regulations, labs can achieve optimal safety outcomes while supporting cutting-edge research. Beyond PPE, it is important that quality and reliability standards are extended to all your labware. A faulty item or unregulated solution could lead to unpredictable outcome in the most basic experiments. Our extensive offerings and expert support make it easier to navigate these complexities and create a culture of uncompromising safety.